by Shawn Narancich, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
by Shawn Narancich, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
Decoupling
With the holiday season in full swing and U.S. investors rejoicing about another year of solid U.S. equity returns, most international investors may be forgiven for feeling like they are getting a lump of coal in their Christmas stocking. In an increasingly decoupled global economy, where China’s growth is slowing and Europe and Japan teeter on the brink of recession, 11 percent returns domestically reflect, in part, the increasingly attractive growth profile of the U.S. economy. What’s surprising is the fact that China’s stock market has risen over 30 percent so far this year, helping buoy emerging market equity returns in a year where stocks have fallen in most foreign markets. Providing better investor access to mainland Chinese equity markets (through linking the Hong Kong and Chinese markets) has helped stimulate investor demand, but the flow of economic data out of the Red Giant remains rather discouraging. Slowing industrial production growth, weaker retail sales, and moribund manufacturing activity all speak to the challenges that Chinese policy makers confront in transitioning the world’s second largest economy from an investment led juggernaut to one better balanced by consumption.
Leading the Way
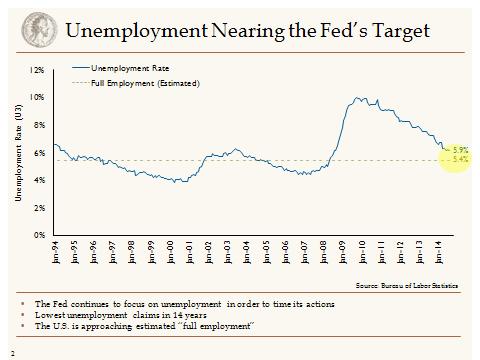
In contrast, the U.S. economy is moving full speed ahead. The November retail sales growth that came in at the high end of estimates reaffirms our thesis of a healthier U.S. consumer boosted by healthy job gains, rising home prices and the falling price of oil. Healthy retail sales data bely the 11 percent sales decline over the long Thanksgiving Day weekend, indicating that the weak sales numbers were more a function of an earlier start to the holiday selling season. With government spending having apparently bottomed and capital spending on the rise, the error of estimates for Q4 GDP is once again higher.
Crude Thoughts
All of which brings us to the topic that seems to be on everyone’s mind nowadays – oil. Now down 46 percent since June, U.S. black gold is far from it at the moment. Yet we continue to believe that the fundamentals of oil aren’t as bad as the price implies. Developed economy inventories are near five-year averages, global demand continues to grow and, most importantly, because of oil’s correlation with economic growth, GDP globally continues to expand in a world of accommodative monetary policy. Contrast today’s environment with 2008, when oil plummeted over 70 percent in eight months, a washout that coincided with consumer price shocks from $4.40/gallon gas and a global economy on the verge of collapse. The best cure for low oil prices is low oil prices, and at today’s level of around $60/barrel, we expect global petroleum exploration and development spending to fall by 25 percent or more in 2015, sowing the seeds for tighter markets and higher prices.
Indeed, evidence of the supply response to come is already upon us. Lower prices are reducing oil companies’ cash flow, leaving them with less money to reinvest in new wells. We are just beginning to see U.S. shale producers announce their 2015 capital budgets and, so far, the anecdotes support our contention that investment levels will drop dramatically. Indeed, November’s new U.S. well permits number, down 45 percent sequentially, offers investors a taste of the supply response to come. Conoco has announced a 20 percent drop in its capital spending and small independent producer Oasis is cutting its 2015 cap ex budget by 44 percent. Dozens of other independent U.S. producers, those responsible for the domestic energy boom of recent years and which are largely responsible for doubling U.S. production over the past six years, will come to the confessional between now and the end of January.
With less money being expended to replenish reserves from shale wells that deplete up to 50 percent of recoverable reserves in the first two years of production, we expect the oil markets to tighten faster than investors currently believe. We would observe that the incremental U.S. liftings that have driven production growth globally are of much shorter duration than the marginal production of 2008 from the Gulf of Mexico. Deepwater projects can take 5-10 years to produce first oil and, when it finally comes, wells under extreme pressure miles below the seafloor produce at persistently high flow rates for project lives that can last up to 30 years. The point is that supply elasticity is likely to bite much faster this time around and, even with the production backdrop pre-shale, low prices didn’t last for long in 2009. So in this festive season, be thankful for the boost to disposable income that today’s low oil prices provide, but don’t expect them to last.
Our Takeaways from the Week
- The U.S. continues to demonstrate its global economic leadership as blue chip stocks prepare to close out another good year
- $60 oil prices provides a meaningful boost to U.S. consumers, but low prices are likely to prove fleeting
Disclosures