“It was a tumultuous end to 2015 with the stock market and the GDP coming out lower than expectations,” said Kellie Holloway, Senior International Trade Specialist with the U.S. Commercial Service.
Under Pressure
Earlier this week we lost a music icon. While I was not a big fan of David Bowie, there are a few songs of his that I enjoy. My favorite is “Under Pressure” which he co-wrote with the band Queen in 1981. The title is very appropriate for what we
Ferguson Wellman Featured in Portland Business Journal
The slowing Chinese economy is ripping through markets, but Ferguson Wellman Capital Management is telling clients not to worry too much because the U.S. economy remains strong.
Happy New Year (?)
As we observe U.S. stocks down roughly 5 percent in the first week of 2016, we are reminded of what occurred last fall when Chinese growth concerns and a strong dollar reverberated around the globe. While China accounts for only
Monster Mash
 by Ralph Cole, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
by Ralph Cole, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
Monster Mash
No holiday better describes earnings season than Halloween. When companies announce earnings, investors are hoping for treats but often times end up getting tricks. In our view, improving corporate earnings are the catalyst to improving stock market returns in the coming year. As we close out the best month for the stock market since 2011, we should review some of the tricks and treats of earnings season.
Treat
Apple reported earnings earlier this week and beat expectations on almost every level. IPhone sales continue to grow at a robust pace around the world. The company sold 48 million iPhones in the third quarter, up 22 percent from last year. Analysts expect the company to sell 79 million iPhones in the final quarter of the year. Average selling prices of the phones continue to rise, which enhances profitability and will lead to $60 billion in free cash flow this year alone.
Tricks
As expected, the energy sector has had a rough time of it this earnings season. Earnings for the S&P 500 energy sector were expected to be down 73 percent this quarter and that indeed has been the case. During these distressing times all companies begin to dramatically scale back investment and reduce headcount. We feel that higher quality companies with good assets, low debt levels and quality management teams will benefit from the eventual rise in oil prices.
Trick and Treat
In no place is the bifurcations of earnings season more evident than in footwear. Nike reported earnings that beat analyst estimates by 12 percent and the stock responded with a nine percent pop the next day. Nike also reported a solid outlook for the coming quarters as well. Sketchers, on the other hand, tricked investors and missed earnings by a whopping 21 percent last week and the stock dropped 31.5 percent with the news.
Why have stocks responded so positively to a mixed earnings environment? Expectations for third quarter earnings had been lowered so much that companies have been able to meet and often beat those reduced forecasts. Also, the much advertised slowdown in China has not had as big of an impact on earnings as investors feared. While the investment slowdown in China has hurt some industrial companies, the Chinese consumer has actually helped the likes of both Apple and Nike.
Takeaways for the week
- There have been more treats than tricks this earnings season which has driven the S&P 500 higher by nine percent this month
- Earnings season continues to be very volatile and stock selection has been key
Upside Down
 by Ralph Cole, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
by Ralph Cole, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
Upside Down
This has been one of the most interesting trading weeks of the year. The seasonal pattern of the stock market is to bottom in October, and rally through the end of the year. While this doesn’t happen every year, so far in October we are following that script. The S&P 500 sold off sharply following the Fed’s decision not to raise interest rates at the September meeting, but found bottom last Friday and has rallied ever since.
Often times the fourth quarter rally is led by names that have performed poorly in the first three quarters of the year. This week was no exception. Through the first nine months of the year energy, materials and the industrial sectors were down 21 percent, 17 percent and 10 percent respectively. Over the last week energy stocks are up 7 percent, the materials sector is up 6.5 percent and industrials are up 6 percent.
Two questions come to mind: First, why did this happen? Secondly, is it sustainable?
Growth stocks were in favor for the first nine months of the year. This is typical during periods of slow global growth as investors are willing to pay handsomely to get the kind of sales growth we have seen in Netflix, Amazon and the healthcare sector. At some point, these names become very expensive. The global slowdown has been led by China, and this past week economic data has been a little better in that country. Probably not enough to signal a huge change in their economy, but enough to spook investors regarding short positions in the more cyclical parts of the market.
As a firm, we believed that oil prices and the energy sector were due to rally because of supply and demand responses in the energy markets. Specifically, low oil prices have caused gasoline demand to rise here in the U.S., while simultaneously causing a drop off in oil production. Historically this combination has always led to higher oil prices and oil rallied nearly 10 percent this week alone.
Whether or not this change in the trend is sustainable remains to be seen. The developed economies of the world remain the engines of growth of the global economy. Demand from the U.S., UK and Europe need to rescue growth in flagging emerging market economies. We believe that this will be the case in the coming months, but doubt that the market will continue its recovery in a straight line. Slow growth accompanied by Fed uncertainty will lead to continued heightened volatility.
Our Takeaways for the Week
- Fourth quarter rallies are common in the stock market, and so far this quarter we are up nearly 5 percent
- We think global growth will accelerate as we move into 2015, supporting the more cyclical sectors of the S&P 500
Slow Ride
 by Brad Houle, CFA
Executive Vice President
by Brad Houle, CFA
Executive Vice President
I had a terrible first car - a 1978 Honda Wagon. It came equipped with vinyl seats, a manual choke, AM Radio and was a shade of brown that resembled a very well-worn Buster Brown shoe from that time. Growing up in Montana, the 1978 Honda wagon also did not like to start in below zero weather. It required stomping on the gas several times and pulling out the manual choke as far as it would go. The Wagon had all of 60 horsepower which made driving up a hill or passing another car a tenuous endeavor and frequently required putting the gas pedal all the way to the floor. There was no difference in the Honda's power if the pedal was depressed completely to the floor versus let off a little. The same could be said for the Federal funds rate being effectively zero or .25 percent. There is not much difference in the impact on economic growth.
On Thursday, the Federal Reserve left the Fed funds rate unchanged, citing global growth concerns. Ultimately, this move seems to be more about the messaging to the markets rather than actually being impactful to economic growth. The Fed does not want to further upset the applecart given recent volatility in world markets by appearing too hawkish and therefore causing financial market participants to fear the Fed will tighten too aggressively.
The Fed funds rate is important as it is one of the tools the Federal Reserve has to stimulate or slow down the economy. Should there be an external shock that requires intervention, with short term interest rates at or near zero, the Federal Reserve has no "dry powder" to stimulate the economy. As such, the Federal Reserve is highly motivated to normalize interest rate policy to allow more flexibility should a crisis arise that requires them coming to the rescue.
With all the hand wringing around when the first rate hike since 2006 will occur, it is also important to remember that a rate increase is good news. It means that the economy is strong enough that the Federal Reserve wants to make certain that it does not get overheated. The labor market has finally healed from the financial crisis and our economy continues to grow.
Our Takeaways for the Week:
- Domestically our consumption driven economy is doing well with a strong labor market and inflation that is well in hand.
- Internationally, the economic uncertainty in China and resulting turbulence in emerging markets has caused the Fed to remain on hold
Keep Calm and Carry On
 by Shawn Narancich, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
by Shawn Narancich, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
Feeling Violated
Worries about competitive currency devaluations emanating from China’s small haircut to the yuan last week were supplanted this week by manufacturing related fears that the world’s second largest economy could be experiencing a hard landing. The result was a tough week for equity investors, as European stocks entered correction territory and U.S. stocks fell five percent.
Timing is Everything
As the sell-off accelerated into today’s close, we couldn’t help but wonder what market soothing policy moves the Chinese might institute next, nor could we ignore the palpable sense that the Fed’s lift-off from zero interest rate policy just got delayed again. Volatility in stocks will register with Yellen & Co. as they attempt to time this cycle’s first interest rate hike. However, more impactful will be the continued deflation in commodities that threatens to leave the price level far from the Fed’s stated goal of two percent inflation. As oil seeks out new cyclical lows and Treasuries benefit from a flight-to-quality bid, the trade-weighted dollar actually declined today. At a time of increased economic and market turmoil overseas, this hints of US monetary policy remaining easier for longer.
Reasons For Optimism
Low fuel prices and an increasingly healthy job market are combining to boost the collective spending power of U.S. consumers, helping drive the economy to what we believe will be a stronger second half of the year. Notwithstanding this week’s pullback in stocks, we look forward to a better second half of the year for corporate America, which should benefit from easier foreign currency comparisons and a turnaround in oil prices, two key factors that have helped keep earnings flat so far this year. As profit visibility improves, we expect stocks to make forward progress.
Ringin’ the Till
With all but a small number of companies having now reported, the sun is setting on a second quarter earnings season characterized again by companies under promising and over delivering. Retailers book-ended Q2 numbers this week by reporting a decidedly mixed bag of results. While America’s largest retailer struggles to grow, Wal-Mart’s rival Target came through with earnings just strong enough to make investors believe that this beleaguered retailer has put the worst of its merchandising and credit breech struggles behind it. Standing out to the upside was Home Depot, which reported another impressive quarter of sales driven by higher house prices and rising home improvement spending. While closing down for the week amidst market turmoil, Home Depot’s stock outperformed the broader market as management once again raised its profit forecast for the year.
Our Takeaways from the Week
- A sell-off in global equities pierced the veil of U.S. market tranquility
- Retailers concluded second quarter earnings season by reporting mixed results
All the Beer in China
 by Brad Houle, CFA
Executive Vice President
by Brad Houle, CFA
Executive Vice President
Currency markets are extremely difficult to grasp and most people’s experience with foreign currency is limited to travel. These experiences generally involve moments where someone realizes they just paid roughly six dollars for a Diet Coke at the Eiffel Tower or that they can buy a substantial amount of beer for the equivalent of a dollar in China. This week the news that China had devalued its currency the renminbi or (RMB) by two percent was headline financial news and drove market volatility around the world. Two percent is not a lot of anything so why does this matter so much? On the surface, having a strong economy and a strong currency should be the goal of every country. However, in times of economic weakness central governments only have a few leavers to pull to stimulate economic growth.
One of the obvious and favorite methods is to stimulate economic growth to lower interest rates. This has been done in the United States since the financial crisis and numerous other governments around the world have used this play from the economic rescue playbook. One of the other techniques is to have a weak currency. Having a weaker currency gives a country a potentially large economic tailwind because it makes goods that are exported from the country with a weak currency relatively less expensive when exported to a country with a stronger country. To use a beer analogy, Tsingtao beer from China is normally 8 dollars a six pack at the supermarket and Stella Artois from Belgium is also around the same price. If China devalues its currency, the beer distributor can then buy Tsingtao for a discount because the U.S. dollar buys more Chinese RMB and therefore more Tsingtao. The relative price of the Tsingtao is now less than the Stella Artois and consumers will substitute the less expensive good for the more expensive good. It can be broken down to an ECON 101 scenario of supply and demand and consumer preference. If you then multiply this effect by a billions of dollars of exports from China or another country devaluing its currency it becomes impactful.
Officially, most countries profess to maintain a strong currency policy as that is often associated with a strong economy. Zhang Xiaohui, an assistant governor of the central bank of China, was quoted in The New York Times stating that the RMB is a strong currency and there was "no basis for the continued depreciation of the renminbi." The decision to depreciate the RMB was characterized by the Chinese government as a move to make the currency more market-oriented.
The fear by investors is that this is a sign that China is struggling to keep its economy growing. While China's last GDP growth number was 7 percent year-over-year, there have been worries about the Chinese economy slowing and that the actual growth rate was materially lower than what was “officially” reported. Data has been mixed relative to economic growth in China with worries about a property market bubble and economic indicators such as auto sales being very weak.
Our Takeaways for the Week
- Currency devaluation can be positively impactful to economic growth as it creates a tailwind for an export economy
- The signal that the markets took from the Chinese currency devaluation this week was that the growth in China is possibly weaker than the government was officially reporting
Smoke and Mirrors
 by Brad Houle, CFA
Executive Vice President
by Brad Houle, CFA
Executive Vice President
Gyrations in the Chinese A-share stock market have been a big topic in the financial press recently. The questions that we are getting from clients all center on what the broader implications might be for the Chinese economy and the impact on Western economies. Bottom line, the Chinese A-share market gyrations are a circus side show that will not have real impact on the actual economy of China or the economies of the U.S. or Western Europe.
In fact, the recent events in the Chinese stock market are an excellent primer on what NOT to do while trying to develop free price capital markets. Currently, the A-share market is more rigged than a game of Three-card Monte and the government in Beijing is determined to build the world’s biggest casino. There has been a dizzying array of strategies employed by the Chinese government to first inflate the value of the market and then attempt to control its inevitable decline. Most investors in the A-share markets are Chinese retail investors. The use of borrowed money or margin was encouraged and the A-share market became the most levered financial market of all time for a short while. Since the market started its downward slide, margin debt has now been restricted. In addition, if you are a greater than 5 percent holder of a stock, you are now not allowed to sell for six months. In addition, 200 companies listed on the Shanghai exchange have suspended trading. This is only a partial list of the heavy handed tactics utilized by the government in an attempt to control the stock market. Capital markets that are free from unnecessary regulation and are as transparent as possible are vital to build trust with global investors. While China has gotten it wrong in the short-term, eventually they will get it right as the country transforms to more of a free market economy.
The Chinese A-share market is a rounding error in international equity indexes and Chinese exposure for our clients is accomplished via exposure to Hong Kong and its stock market’s H-shares, as well as Chinese companies that trade on American exchanges. Unless you are a retail investor in China who is invested in the Chinese A-share market, it is not impactful. What is important, however, is what happens in the Chinese economy.
Chinese GDP was released this week at a 7 percent year-over-year growth rate. It is an old story that global investors look at Chinese economic data with skepticism. If you look deeper at other economic indicators in China, the data suggests that a number much lower than 7 percent GDP is probably closer to the truth. One of our research partners, Cornerstone Macro, points out that as business confidence is at the lowest level in 16 years, electricity consumption is up just 1.8 percent, auto sales are down 40 percent and bank loan demand is lower. As such, Cornerstone theorizes that actual GDP growth is likely closer to 5 percent. China is the number two economy in the world, and what happens with the trajectory of the Chinese economy is impactful to the world economy. Currently, the U.S. and European economies appear to be decoupled from the Chinese economy and are benefiting from lower commodity costs and strong domestic economies.
Our Takeaways for the Week
- The Greek parliament voted to enact reforms agreed upon with the European Union this past Thursday. Once again, the “can” of the Greek Financial Crisis is getting kicked down the road
- The Chinese A-share market is unimportant in the global economy. Performance of the broader economy in China is of vital importance to the world economy and the trajectory of growth or lack of growth is something we are monitoring closely
Patience
 by Ralph Cole, CFA
Executive Vice President of Research
by Ralph Cole, CFA
Executive Vice President of Research
Patience
It’s been a strange week in “Euroland.” After a resounding “no” vote on the Greek debt bailout referendum last Sunday, it appeared that Greece was on its way out of the Eurozone. Capital markets promptly sold off early in the week.
Today it appears that Greece has delivered a reasonable response. “The program they are presenting is serious and credible,” said French President François Hollande.
We must admit that we have a tad bit of Greek fatigue in recent weeks, but it is clear that Greece is on everyone’s mind these days. The country has presented a 3-year plan, which is better than some of the temporary schemes that have been floating around the past few months. If it is accepted over the weekend, markets should continue to move higher along with yields. The removal of this distraction will allow the ECB to continue focusing on the nascent European recovery.
We continue to have our doubts for the long-term sustainability of Greece within the Eurozone. It doesn’t appear to us that the Greek people are committed to the structural changes that need to take place in order to pay their debts and make their economy more competitive in the future. This will not be the last time we talk about Greece’s debt, economy and leadership.
Roller Coaster
Compounding the volatility induced by Greece was the roller coaster known as the Chinese A-share market. As China tries to open its capital markets, they also must learn how to govern them. Much like holding water in your hands, the tighter you grip, the more water that slips through your fingers. Confidence in the system is the most important element to a successful exchange. The more China tries to prop up their market the less confidence investors have in their system.
We are more concerned with underlying growth in China’s economy than we are with the volatility in their A-share market. It is clear that China’s growth is slowing and it is nowhere near the 7 percent reported by the Chinese government. Growth around the world is challenged and China’s growth is needed until the stimulus by other countries gets their economies growing.
We will continue to monitor their real economy closely in the coming months. We expect growth to pick up around the world in the second half of the year, but that forecast has come into question in recent weeks.
Our Takeaways for the Week
- Proper investment patience kept prudent investors from overreacting in a week packed with news flow
- Growth in the second half of the year should propel markets modestly higher
Black Gold?
 by Shawn Narancich, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
by Shawn Narancich, CFAExecutive Vice President of Research
Decoupling
With the holiday season in full swing and U.S. investors rejoicing about another year of solid U.S. equity returns, most international investors may be forgiven for feeling like they are getting a lump of coal in their Christmas stocking. In an increasingly decoupled global economy, where China’s growth is slowing and Europe and Japan teeter on the brink of recession, 11 percent returns domestically reflect, in part, the increasingly attractive growth profile of the U.S. economy. What’s surprising is the fact that China’s stock market has risen over 30 percent so far this year, helping buoy emerging market equity returns in a year where stocks have fallen in most foreign markets. Providing better investor access to mainland Chinese equity markets (through linking the Hong Kong and Chinese markets) has helped stimulate investor demand, but the flow of economic data out of the Red Giant remains rather discouraging. Slowing industrial production growth, weaker retail sales, and moribund manufacturing activity all speak to the challenges that Chinese policy makers confront in transitioning the world’s second largest economy from an investment led juggernaut to one better balanced by consumption.
Leading the Way
In contrast, the U.S. economy is moving full speed ahead. The November retail sales growth that came in at the high end of estimates reaffirms our thesis of a healthier U.S. consumer boosted by healthy job gains, rising home prices and the falling price of oil. Healthy retail sales data bely the 11 percent sales decline over the long Thanksgiving Day weekend, indicating that the weak sales numbers were more a function of an earlier start to the holiday selling season. With government spending having apparently bottomed and capital spending on the rise, the error of estimates for Q4 GDP is once again higher.
Crude Thoughts
All of which brings us to the topic that seems to be on everyone’s mind nowadays – oil. Now down 46 percent since June, U.S. black gold is far from it at the moment. Yet we continue to believe that the fundamentals of oil aren’t as bad as the price implies. Developed economy inventories are near five-year averages, global demand continues to grow and, most importantly, because of oil’s correlation with economic growth, GDP globally continues to expand in a world of accommodative monetary policy. Contrast today’s environment with 2008, when oil plummeted over 70 percent in eight months, a washout that coincided with consumer price shocks from $4.40/gallon gas and a global economy on the verge of collapse. The best cure for low oil prices is low oil prices, and at today’s level of around $60/barrel, we expect global petroleum exploration and development spending to fall by 25 percent or more in 2015, sowing the seeds for tighter markets and higher prices.
Indeed, evidence of the supply response to come is already upon us. Lower prices are reducing oil companies’ cash flow, leaving them with less money to reinvest in new wells. We are just beginning to see U.S. shale producers announce their 2015 capital budgets and, so far, the anecdotes support our contention that investment levels will drop dramatically. Indeed, November’s new U.S. well permits number, down 45 percent sequentially, offers investors a taste of the supply response to come. Conoco has announced a 20 percent drop in its capital spending and small independent producer Oasis is cutting its 2015 cap ex budget by 44 percent. Dozens of other independent U.S. producers, those responsible for the domestic energy boom of recent years and which are largely responsible for doubling U.S. production over the past six years, will come to the confessional between now and the end of January.
With less money being expended to replenish reserves from shale wells that deplete up to 50 percent of recoverable reserves in the first two years of production, we expect the oil markets to tighten faster than investors currently believe. We would observe that the incremental U.S. liftings that have driven production growth globally are of much shorter duration than the marginal production of 2008 from the Gulf of Mexico. Deepwater projects can take 5-10 years to produce first oil and, when it finally comes, wells under extreme pressure miles below the seafloor produce at persistently high flow rates for project lives that can last up to 30 years. The point is that supply elasticity is likely to bite much faster this time around and, even with the production backdrop pre-shale, low prices didn’t last for long in 2009. So in this festive season, be thankful for the boost to disposable income that today’s low oil prices provide, but don’t expect them to last.
Our Takeaways from the Week
- The U.S. continues to demonstrate its global economic leadership as blue chip stocks prepare to close out another good year
- $60 oil prices provides a meaningful boost to U.S. consumers, but low prices are likely to prove fleeting
Easy Money
 by Ralph Cole, CFA
Executive Vice President of Research
by Ralph Cole, CFA
Executive Vice President of Research
The global economic expansion continues to run at very different speeds around the world. However, the common thread among most all developed economies has been easy money. Today, China joined the party by lowering interest rates for the first time since 2012. The reasons for lower rates has been stubbornly slow growth, and as long as inflation remains low, central banks can feel confident in their choice to stimulate their economies.
Markets were also buoyed this week by dovish comments out of the European Central Bank. With most European economies mired in little to no growth, and the ECB has embarked on its own version of quantitative easing (QE). Mario Draghi hinted in a speech yesterday that their asset-buying program could expand if necessary. The lack of economic growth in Europe can at least be partially explained by Draghi’s habit of speaking about, rather than actually enacting, central bank policy. In Texas, they would call this “all hat and no cattle”.
Thrift Shop
This week just about wrapped up earnings season for retail companies. Earnings were basically strong across the board for retailers from Dollar Tree and Target to Foot Locker and Best Buy. We believe retailers and consumers are starting to feel the benefits of lower prices at the gas pump. Lower gas prices often coincide with higher consumer confidence numbers, which in turn leads to increased consumer spending.
What makes the retail industry so interesting is the plethora of stores from which shoppers have to choose. I don’t think any of us would argue that we aren’t over-retailed in the U.S. This abundance is one reason we don’t see much inflation. Despite a zero percent interest rate policy and a massive expansion of the Fed’s balance sheet, inflation is not yet finding its way onto store shelves. Competition for the consumer’s discretionary dollar remains fierce. Case in point: the phenomenon of Black Friday sales moving earlier into our Thanksgiving holiday week.
Our Takeaways from the Week
- Global markets continue to respond positively to easy money policies around the world
- Lower gas prices should lead to positive sales for retailers this Holiday season
- Have a Happy Thanksgiving and travel safely
Slow Ride
 by Jason Norris, CFA
Executive Vice President of Research
by Jason Norris, CFA
Executive Vice President of Research
Slow Ride
This week, the World Bank lowered their global GDP assumptions for 2014 to 2.8 percent from 3.2 percent. The bank cited the BRICs (Brazil, Russia, India and China) as well as the U.S. as culprits for the lowered estimates. We believe the slowdown in the U.S. is solely a first quarter event due to weather, and we expect to see acceleration throughout the year. China’s growth, though slowing, is still relatively robust and inflation remains under control. Regrettably, Brazil and Russia have not fared as well. As the chart below highlights, Brazil and Russia are stuck in a slowing growth, high inflation environment that is difficult to overcome. With high inflation, there is pressure to raise interest rates, but that leads to increased headwind for growth.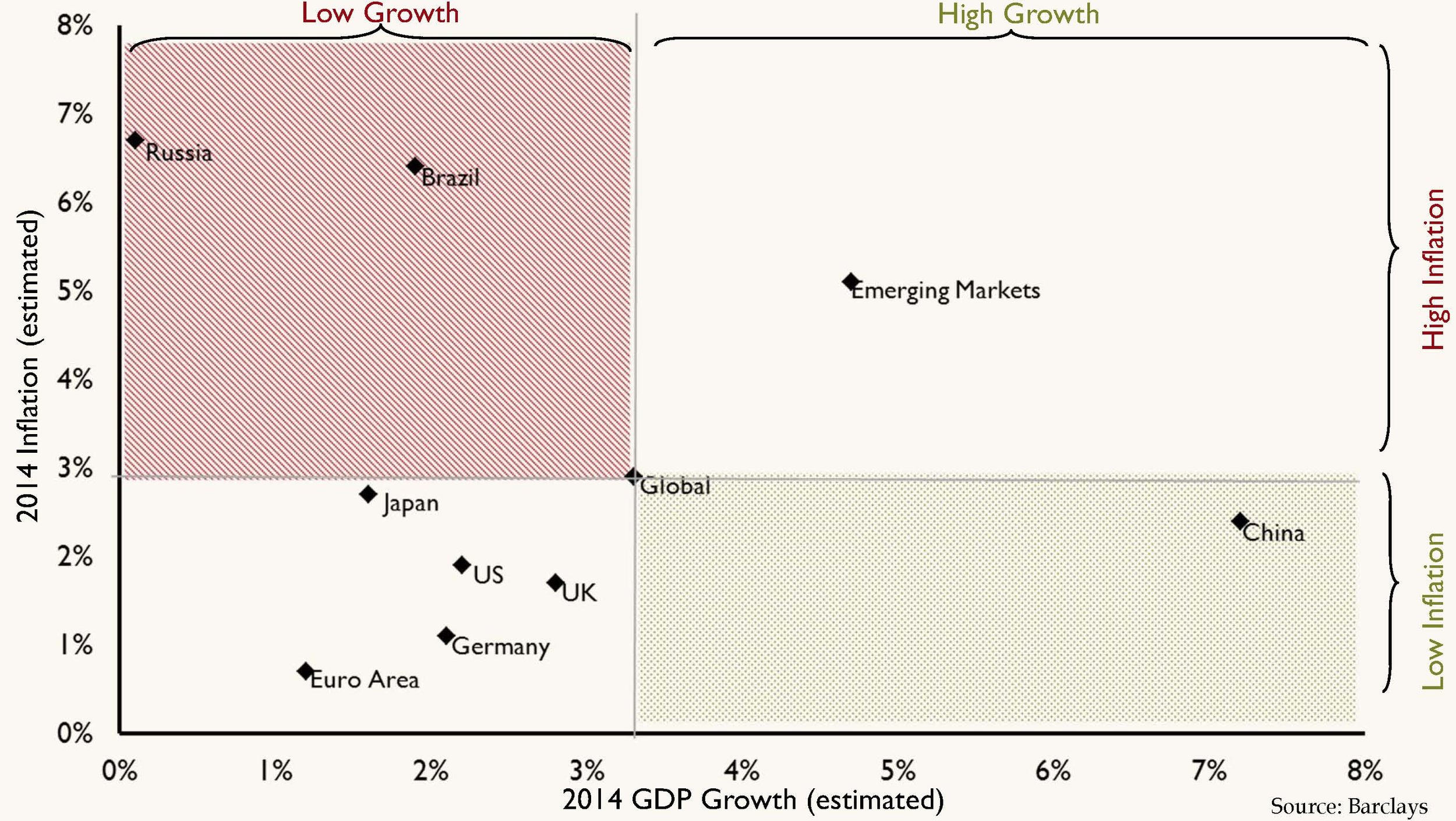
Unfortunately for Brazil, the build up for the World Cup has not provided the added stimulus that was hoped for. Corruption and cronyism have proved to be rampant and the economy has not seen the desired lift. There was the expectation that the employment opportunities would bring about an economic boost for their citizens. However, this hasn’t happened and there remains strong sense of frustration among the public.
London Calling
Earlier this week, there were protests centered in London (with minor demonstrations in Paris and other European cities) due to the growth of the online transportation company, Uber. This company is disrupting the “old” taxi cab model by allowing customers to access drivers of vehicles for hire through a mobile app. This disruption allows consumers to by-pass the classic taxi for a private hire, which in many instances, may be cheaper and more convenient. The company started in San Francisco and is expanding globally.
The protests may have had an unintended counter effect. A lot of the general public, especially in Europe, have not heard of Uber, thus these actions just put the start-up on the front pages. Competition for the general public is usually a good thing in pushing prices down and improving service. However, as a CNBC reporter stated, the French public are in favor of the protests, but that doesn’t come as a surprise “in a country where competition is not really a key word and where a strike is probably some sort of national sport.” On a final note, Uber recently completed a round of financing which valued the company at close to $18 billion.
The Mob Rules
While stocks hit new highs at the beginning of the week, geopolitical issues in the Middle East have tempered those gains. With militants gaining control of key cities in Iraq, the supply of oil has now come into question. This has resulted in a run up in the price of crude. We are of the belief that the price of oil will remain stable as the U.S. continues to increase its supply over the long term. However, we will continue to experience short term volatility due to global tensions and we remain overweight the energy sector based on our thesis that the global economy remains in expansion mode. This recent spike has resulted in the sector being the best performer this last week.
Takeaways for the Week
- Key emerging markets are struggling with flagging growth and high inflation and investors have to be selective
- In aggregate, global growth is still healthy and the U.S. should lead the developed world
- The U.S. will make it out of the first round of the World Cup and Germany will win it all









